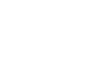Forecast Origin Dates
J-SCOPE forecast results for the simulation beginning in April of 2024 are shown through a series of figures below. In the first figure, each panel represents ensemble averaged anomalies of two month averages for the region. In the second figure, the panels depict the relative uncertainty from the ensemble for the same time periods.
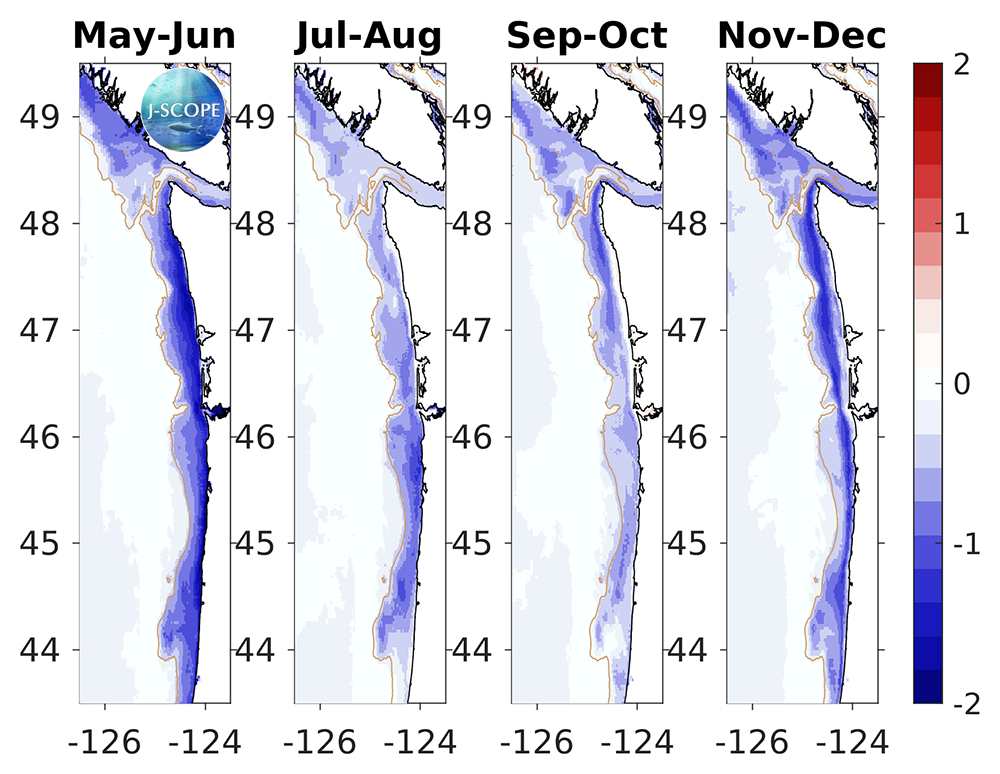
From the maps, oxygen is forecasted to be lower than the climatology during the upwelling season of 2024 (May-Aug) in Washington and Oregon with the maximum anomaly occurring at the onset of the the upwelling season. The relative uncertainty remains low (10%) until the end of the upwelling season (September-October) when the relative uncertainty gets higher (up to ~50%) and remains high until the end of the year.
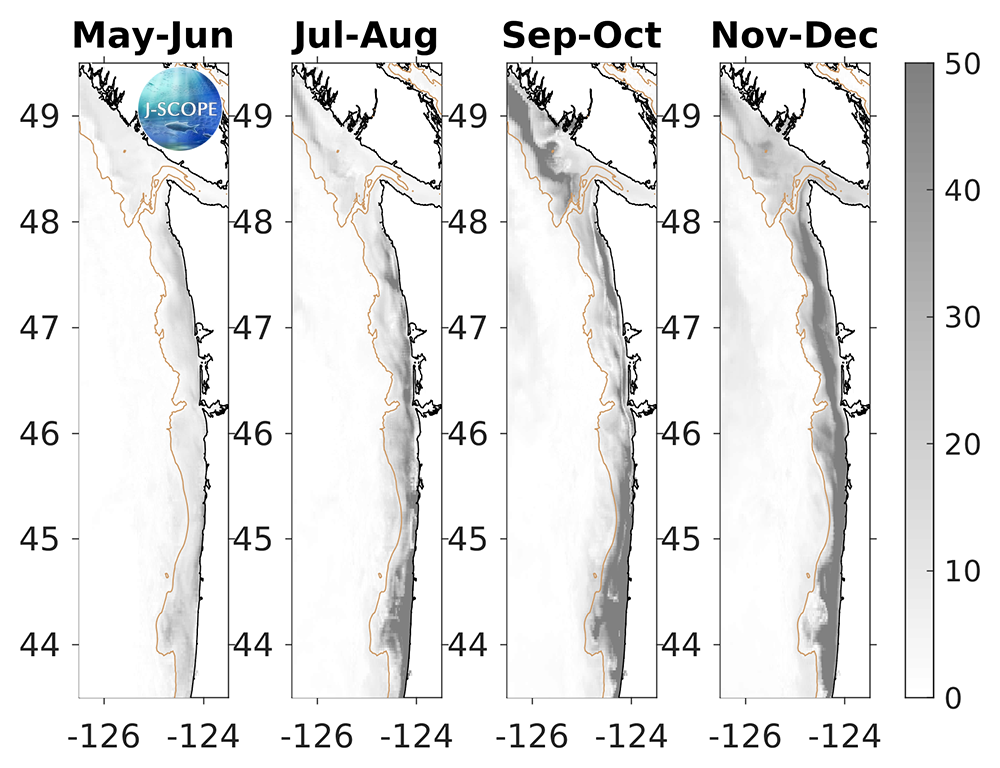
Forecasted bottom oxygen (mg/l), averaged over three ensemble members for each month, indicates declines in oxygen concentrations over the course of the forecast for both Washington and Oregon, with hypoxia (O2 < 2 mg/l) prominent over about the outer shelf of Oregon in May and expanding to much of the entire Washington and Oregon shelves in June and persisting through September eventually overtaking the typically normoxic region at the northern boundary of the Washington shelf around Ćháʔba·.
Hypoxia extends upward into the water column as well. The percentage of the water column that is forecasted to experience hypoxia (O2 < 2 mg/l) is a metric for this phenomenon. Early in the upwelling season, hypoxia is forecasted to occupy a small percentage of the water column over the entire modeled region (<10%). In July, some regions in Oregon, begin to experience more than ~20%. Over the course of the summer, the percentage of the water column that is hypoxic increases mostly in Oregon, with particularly high volumes forecasted for Heceta Bank on the Oregon shelf and south of Cape Elizabeth in August and September with values exceeding 50% of the water column experiencing hypoxia.
Time series of bottom oxygen from the Washington coast near one of the Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary (OCNMS) moorings at Cape Elizabeth (site CE042), from NH-10 mooring off of Newport, Oregon, and from the Ćháʔba· mooring off of La Push, Washington, are shown for each member of the ensemble. The model forecasts that hypoxia will most likely develop at all three moorings. At the NH-10 mooring, hypoxia is forecasted to begin in mid June/early July, which is more than one month before the climatological onset of hypoxia (green). Further north, at the CE042 mooring, hypoxia is forecasted to begin in early June to mid June, which is more than one month before the climatological onset of hypoxia (green). Another time series from the outer Washington shelf, Ćháʔba·, forecasts hypoxia onset for all three ensemble members in August is unusual for this location and there is not typically hypoxia observed at this location.
Finally, climatological cross-sections from the Newport Line in Oregon (44°N) and the Grays Harbor Line in Washington (47°N) are compared to the forecasted average of the ensemble members during the summer upwelling season (May-August). In both Oregon and Washington, the forecast projects that the oxygen concentration for the upwelling season of 2024 will be lower than the climatology on both the shelf and at deeper depths, with the largest anomalies occurring between ~50 m and ~300 m depth in Oregon, and ~50 m and 250 m depth in Washington.
The emergence of anoxia in the model in late summer is caused by a bias associated with the lack of relaxations in the winds (found to be important in a paper by Adams et al, 2013) in the Climate Forecast System input files as well as a bias in the shortwave radiation (see 2013, Year in Review). The model does have skill in predicting the emergence and severity of hypoxia, while it is biased low for these reasons. Given the difficulty in predicting the fall transition in prior forecasts (see 2013, Year in Review), the forecast for low oxygen levels forecasted well into August is highly uncertain.
The modeled region bottom oxygen (ml/l) anomaly averaged over all three ensemble members and in time for (from left to right) May-June, July-August, September-October, November-December.
The relative uncertainty in percent for the modeled region bottom oxygen values averaged in time for (from left to right) May-June, July-August, September-October, November-December.. The relative uncertainty is defined as the standard deviation of the ensemble divided by the mean of the ensemble and is reported as a percentage of the mean.
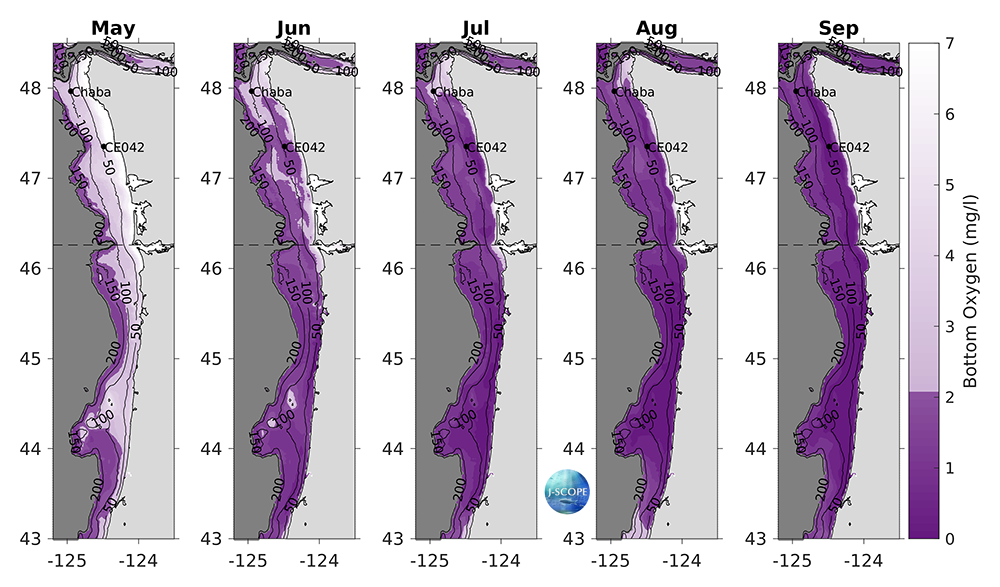
The modeled region bottom oxygen (mg/l) averaged over all three ensemble members and in time for (from left to right) May, June, July, August, and September. Hypoxia (O2 < 2 mg/l) is shown in dark purple, land is shown in light grey, and offshore areas are shaded dark gray. The black dashed line indicates the boundary between Washington and Oregon waters. Black contours indicate bathymetry on the shelf. Two mooring locations are plotted for reference (Ćháʔba·, CE042).
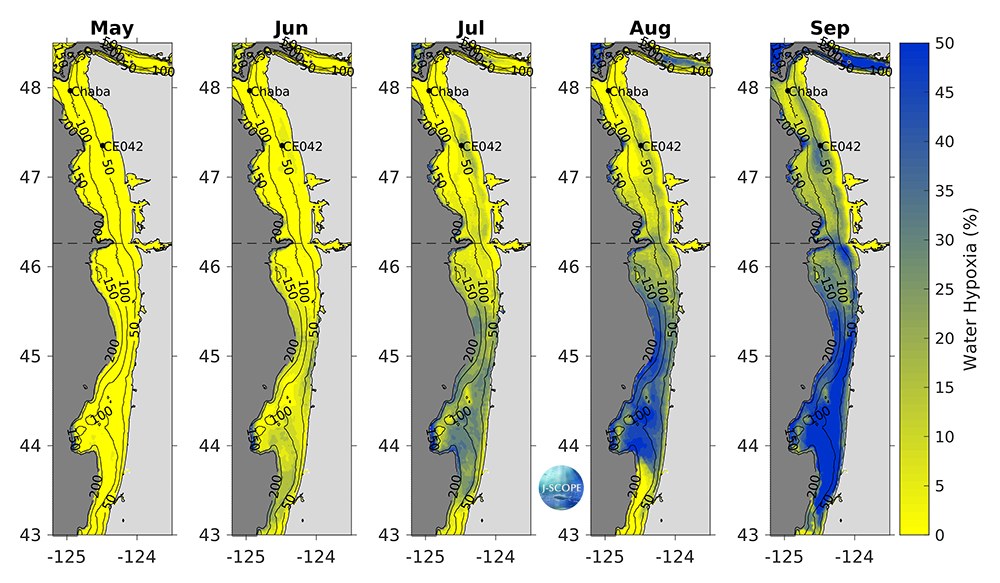
The modeled region water column hypoxia (%) averaged over all three ensemble members and in time for (from left to right) May, June, July, August, and September. Land is shown in light grey, and offshore areas are shaded dark gray. The black dashed line indicates the boundary between Washington and Oregon waters. Black contours indicate bathymetry on the shelf. Two mooring locations are plotted for reference (Ćháʔba·, CE042).
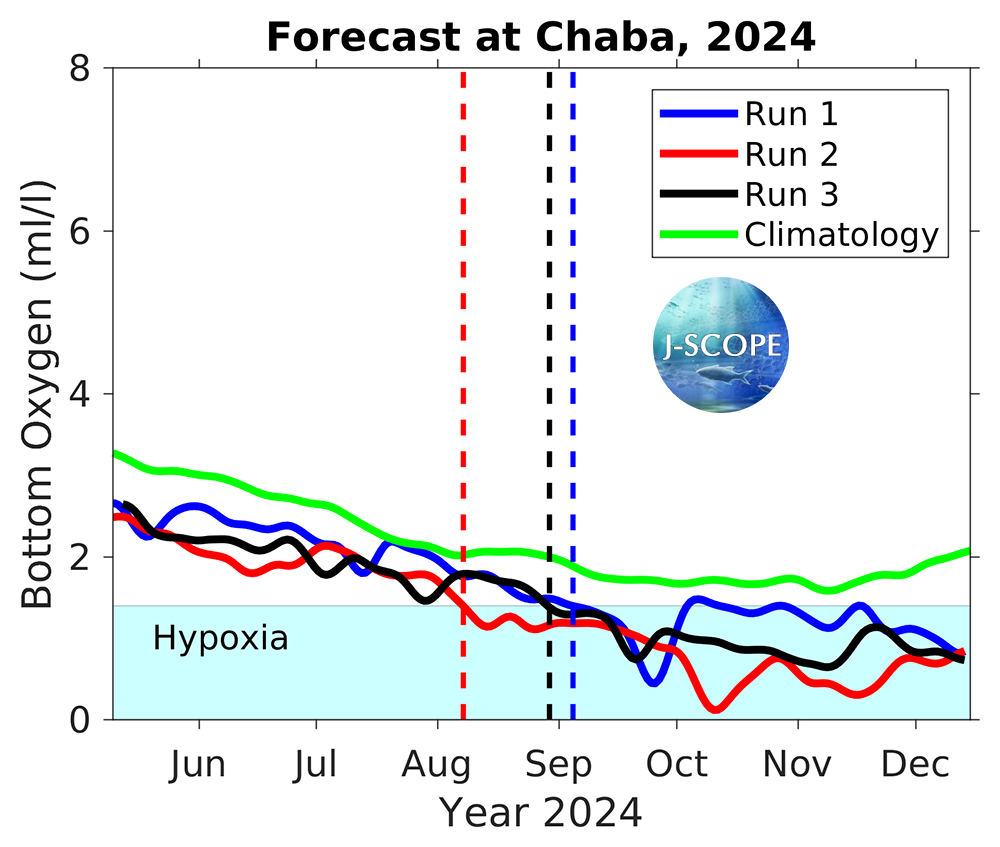
Time series for bottom oxygen at the Ćháʔba· mooring (~48°N) for each of the three ensemble members. Hypoxia is outlined by the blue region on the plot. The timing of each run’s onset of hypoxic conditions for more than 8 days is identified by the vertical dotted lines, with the green line indicating the climatological timing.
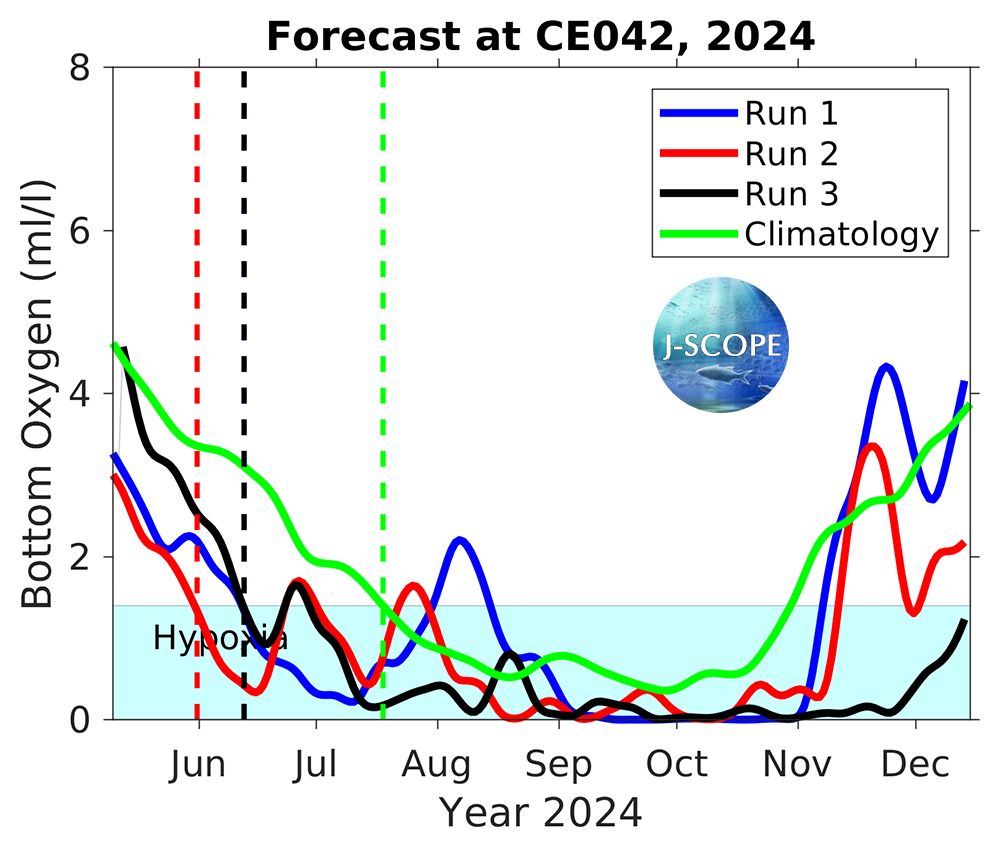
Time series for bottom oxygen at one of the Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary Moorings (CE042, ~47.5°N) for each of the 3 ensemble members. Hypoxia is outlined by the blue region on the plot. The timing of each run’s onset of hypoxic conditions for more than 8 days is identified by the vertical dotted lines, with the green line indicating the climatological timing.
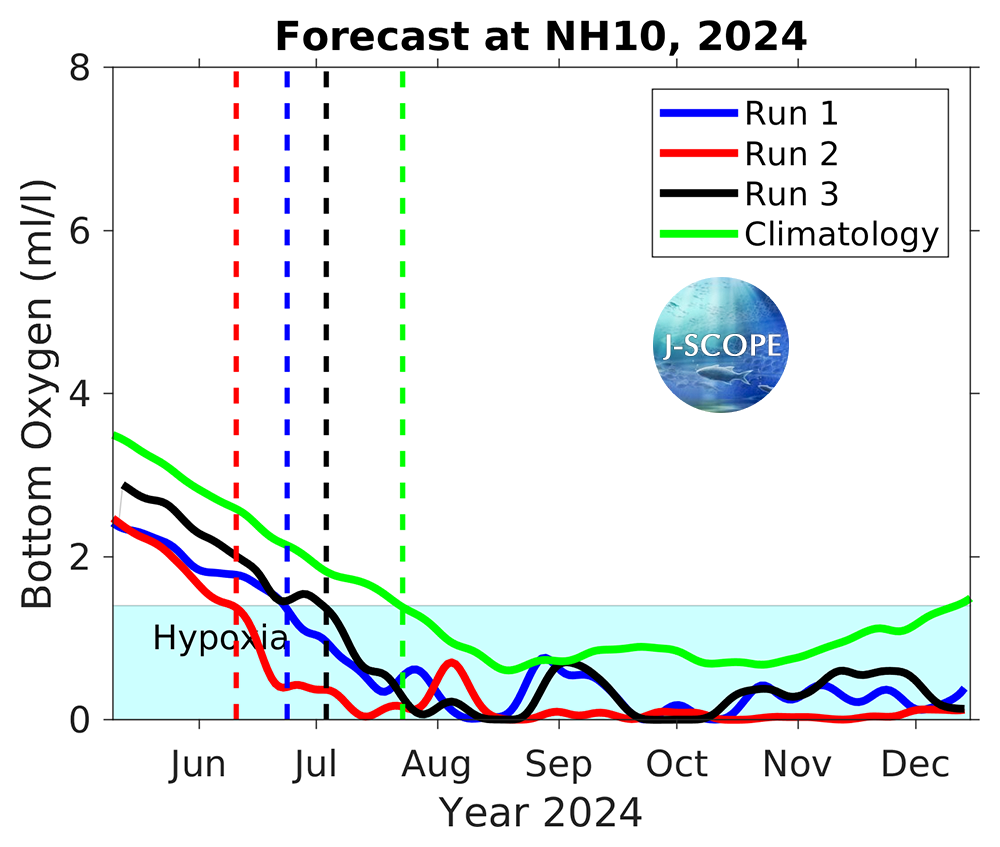
Time series for bottom oxygen at the NH-10 mooring in Oregon (~45°N) for each of the three ensemble members. Hypoxia is outlined by the blue region on the plot. The timing of each run’s onset of hypoxic conditions for more than 8 days is identified by the vertical dotted lines, with the green line indicating the climatological timing.
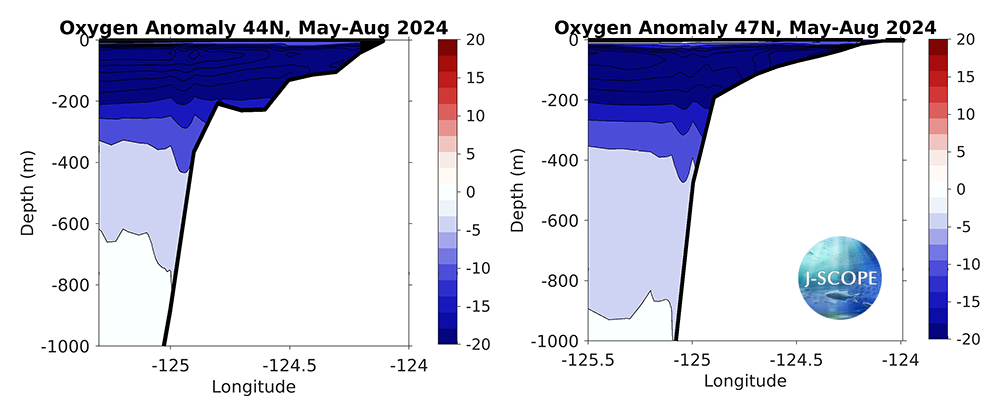
The modeled cross-section from the Newport Line off Oregon (left, 44°N) and the Grays Harbor Line off Washington (right, 47°N), averaged over all three ensemble members, and averaged over the summer upwelling months (May-August).